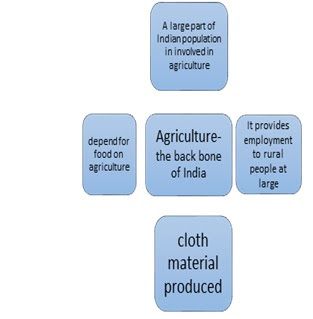
The post English For MPSC is helpful for all kinds of competitive exams as well as to improve general understanding of English. Options in bold letters are the answers. Grammar for MPSC.
1. You ought to be considerate towards your patients’.
The model auxiliary italicized in the sentence above conveys
(a) necessity (b) moral duty (c) obligation(d) mild compulsion
2. Read the following sentence carefully and answer the given question:
“The Captain and Coach of the hockey team attended the press conference”. What is the status of captain and coach in the sentence?
(1) Captain and Coach are two different persons
(2) Captain and Coach is the same person
(3) Captain and Coach are enemies of each other
(4) Captain and Coach are friends
3. He said to me, “Help him in settling the accounts”.
3. Which of the following sentences correctly changes the sentence above into an Indirect speech?
(a) He told me to help him in settling the accounts.
(b) He persuaded me to help him in settling the accounts,
(c) He requested me to help him in settling the accounts.
(d) He urged me to help him to settle the accounts.
4. Grishma spoke with white heat.
Select the correct meaning of the italicized.
(1) Natural shrewdness
(2)Intense passion
(3) Plain voice
(4)Cunning passion
5. The word ‘avaricious’ is synonymous with
(a) applicable (b) omnipresent (c) omniscient (d) greedy
6. “One who lives for pleasure“. Which of the following words matches the meaning above?
(a) Fanatic (c) Hedonist
(b) Happy-go-lucky (d) Misogynist
7. “Stop talking“.. Which of the following sentences changes the above imperative sentence into an interrogative sentence?
(a) Did you stop talking?
(b) Would you stop talking?
(c) Will you stop talking?
(d) Shall you stop talking?
8. Use proper punctuation in the blank space of the following sentence:
I have no money —-therefore I cannot afford a servant.
(1) , (comma)
(2): (colon)
(3): (semicolon)
(4) – (hyphen)
9. The italicized word in the given sentence is :
“Notwithstanding the late hour, she attended the meeting as scheduled”.
(1) An adverb
(2) Definite article
(3) Preposition
(4) Auxiliary verb
English For MPSC and UPSC
10. Read the sentence carefully and identify what kind of conjunction the italicized word is :
“He is saving some amount each month so that he can pay his college fees”.
(1) Compound conjunction
(2) Correlative conjunction
(3) Coordinating conjunction
(4) Subordinating conjunction
11. The military is going to lay a trap to arrest the terrorists’.
The underlined form in the sentence above is used to convey
(a) intention to perform a certain action in the near future
(b) planned action
(c) action in remote future
(d) a great probability
12. Choose the best meaning of the italicized word.
She pirouetted across the stage.
(1) Ran fast
(3) Spoke loudly
(2) Took a fast turn or spin.
(4) Looked anxiously
13. ————what you can afford.
Complete the sentence choosing the correct alternative.
(1) Work out (2) Work on (3) Work with (4)Work about
14.Match the following homophones – ‘Vein’, ‘Vain’ and ‘Vane’ with their correct meaning:
(a) Vein (i) Weathercock
(b) Vain (ii) Blood artery
(c) Vane (iii) Conceited, proud
(a) (b). (c)
Answer options:
(1) (iii). (i). (ii)
(2) (ii) (iii) (i)
(3) (ii). (i). (iii)
(4) (i). (ii). (iii)
15. Find out the exact meaning of the underlined idiom in the given sentence: “Most of her friends avoid talking to her as she is constantly blowing her own trumpet”
(1) To forget past enmity (3) To be very busy
(2) To put in all possible efforts (4) To boast about self
English For MPSC
16. Read the following sentence.
“Despite her age, she walks steadily“.
The italicized words walks steadily are examples of:
(1) Noun phrase (3) Adverbial phrase
(2) Adjective phrase (4)None of the above
17. Her bank fell down from her purse.
The italicized word in the sentence above means
(a) balance
(b) financial institution
(d) row of keys
(c) side of a river
18. This is the place where the murder was committed”.
The clause underlined in the sentence above is a/an
(a) Adverbial clause (c) Adjective clause
(b) Noun clause (d) Prepositional clause
19. Choose the word/s wrongly spelt.
(a) LACKADAISICAL
(b) LASCIVIOUS
(c) LIBIDINEOUS
20. Choose the incorrect sentence:
(a) He hurt himself. (c) Behave yourself.
(b) James and myself went together.
(d) She did it all by herself.
21. Choose the correct sentence:
(a) The ship was wrecked and every man, woman and child was drowned.
(b) The ship was wrecked and every man, woman and child were drowned.
(c) The ship was wrecked and every man, woman and child are drowned.
(d) The ship was wrecked and every man, woman and child had drowned.
22. ——-is the correct compound noun in the plural form.
(a) Brothers-in-law (c) Brothers-ins-laws
(b) Brother-in-laws
(d)Brethren-in-law
23.Read the following sentence.
“Hearing the knock, she opened the door.”
What kind of synthesizer is the underlined word in the sentence? It is.
(1) a gerund
(2) a participle
(3) an adverbial clause
(4) a noun clause
24.Read the sentences carefully and chose a correct answer from the options given
(a) Milk and honey are a nourishing food.
(b) Milk and honey is a nourishing food.
25. ‘The judge ordered that the accused be set free”.
The sentence above expresses mood.
(a) Subjunctive
(b) Imperative
(c)Indicative
(d) Expressive
English For MPSC
Read the passage given below carefully and answer question numbers 26 to 30 based on it.
Until he was ten, young Alexander Fleming attended the nearby London Moor school. He was then transferred to Darvel school which he attended with his brothers. Alexander learned a good deal about nature during that four-mile downhill hike to school and the four-mile uphill return trip. He was a quick student and at twelve, the age limit prescribed for Darvel school, he was sent to Kilmarnock Academy. Two years later he joined his brothers John and Robert at the home of his elder brother Thomas, who was to become a successful occultist in London. However, the economic success of the family was yet to be and Alexander was forced to leave school for economic reasons. When he was sixteen he obtained a job in a shipping company. Good fortune, however was on his side and on the side of humanity. In 1901, he received a share in a legacy which made it possible for him to return to school. He decided to study medicine.
26. The word ‘legacy’ in the context means
(1) Lottery
(2) Goodwill money
(3) Inheritance
(4) Legal payment
27. Alexander trekked miles everyday to attend Darvel school
(1) Four
(2) Eight
(3) Twelve
(4)Unknown
28. He was a quick student – This means that Alexander
(1) reached school before his brothers
(2) reached the school-leaving age
(3) was a lively student too soon
(4) was a fast learner
29. and at twelve, the age limit prescribed for Darvel school
This in the context means that children were
(1) Not admitted to the school before they were twelve
(2) Admitted to the school at the age of twelve
(3) Allowed to remain in the school only upto the age of twelve
(4) Admitted to the school anytime after the age of twelve
30. Alexander became rich
(1) by working in a shipping company
(2) when his brother became a successful occultist
(3) because he studied medicine
(4) by receiving share in a legacy
Site For MPSC Preparing for MPSC is a challengeable task.