Verb Types
A verb used in forming the tenses, moods, and voices of other verbs is auxiliary verb.
The primary auxiliary verbs in English are be, do, and have. (am, is, are,was, were, do, does, did, have, has, had)
Sometimes primary auxiliary verbs perform the function of main verbs when they stand alone in the sentence.
The modal auxiliaries are can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, and would.
The main verb is also called the lexical verb or the principal verb. The Main verb typically shows the action or state of being of the subject. Main verbs can stand alone, or they can be used with a helping verb, also called an auxiliary verb.
Go through the sentences given below and say whether the underlined verbs are main verbs or primary auxiliary verbs or modal auxiliary verbs.
1.I had a very simple upbringing.
2.I was immensely impressed.
3.I had learnt from my childhood that money did not mean everything in life.
4.He was a convent educated boy.
5.They did all the work in time.
6.I had to achieve a lot in life.
7. I was very thirsty.
8. I had carried with me.
9. We were lucky.
10. I was wearing a red scarf.
11. We had suggested hara-kiri.
12. We were overjoyed to see tiny green leaves.
13. How long shall we continue to live this life of contradiction ?
14. We must remove this contradiction at the earliest possible moment.
15. I don’t know.
16. I can hear voices.
17. You would better go back.
18. Mrs Adis was sitting in the old basket armchair by the fire.
19. ‘D’ company was successful in occupying the eastern portion of Area Collar.
20. The Defense Minister was on his way to Amritsar.
Frame your own ten sentences using these verbs and say their types.
Grammar TensesVerb Types – Transitive and Intransitive Verbs
Transitive verbs have objects. Intransitive verbs have no objects .
She is fetching water. (Present continuous tense)
In this sentence verb ‘fetching’ has object ‘water’. So the verb ‘fetching’ is transitive verb.
Farmers grow (🍅 🍅) tomatoes in the field.
In this sentence verb ‘grow’ has object ‘tomatoes’. So the verb ‘grow’ is transitive verb.
Tomatoes grow in the field.
In this sentence verb ‘grow’ has no object because action does not pass on. So the verb ‘grow’ here is intransitive verb.
Some verbs are transitive and Intransitive depending upon the function in the sentence.
Indicate whether the Verbs in the following sentences are Transitive or Intransitive. Name the Object of each Transitive Verb’ and the Complement of each Verb of Incomplete Prediction.
In the following sentences the verbs in bold types are intransitive , word or group of words in red colour are complements. The underlined verbs are transitive and the words in blue colour are objects.
- The boy stood on the burning deck. Intransitive
- Tony has fallen sick. Intransitive
- The water is very cold.
- The man saw the accident with his own eyes. Transitive The man saw what? The answer is accident.So object of ‘saw’ is ‘accident’
- The baby fell asleep.
- They are French.
- The rumour seems true.
- He did not tell the truth.
- They made her queen.
- The bad boys hide their faults.
- He is hiding behind the tree.
- We patiently waited at the station.
- The bird flew down and took away the cheese.
- Our children like sweets.
Do it yourself.
Verb Types – Transitive and Intransitive Verbs
- The peon rang the bell.
- The bell rang after the first period.
- Sam sang a beautiful song.
- They sang well in the function.
- Who has broken the window?
- The windows broke in the storm.
- She called her servant a fool.
- His parents named her Patricia.
- He painted the box red.
- You look sad.
- The milk turned sour.
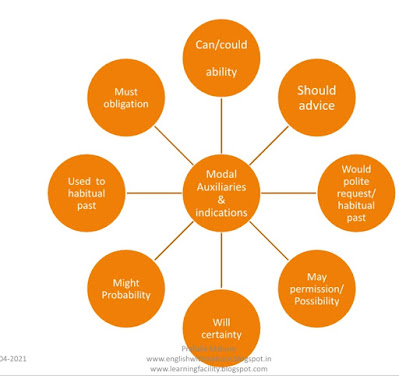
Read the following sentences and observe the use of modal auxiliary .
1. May I speak to you for a moment? ‘May’ indicate permission.
2. She can speak fluent German. ‘can’ — ability
3. He might get angry at first, but hopefully he will understand your situation. ‘might’- probability
4. You should try doing more exercise regularly. ‘should’ – advice
5. Now recruits shall report to the sergeant at 9 am. Shall—certainty
6. I must go home now. It’s late. Must- obligation
7. Could you put this book on the shelf, please? Could – polite request
क्रीयापदाला सहाय्य करणार्या क्रियापदांना सह्याकारि क्रियापदे म्ह्णतात.
be, am, is, are, was, were, do, does, did, have, has, had, shall, will, should, would, can, could, may, might, must, etc.
उपयोग.
1. am, is, are यांचा उपयोग Present Continuous Tense मध्ये व Simple Present Tense च्या Passive Voice मध्ये करतात.
2. was, were यांचा उपयोग Past Continuous Tense मध्ये व Simple Past Tense च्या Passive Voice मध्ये करतात.
3. do,does, did यांचा उपयोग प्रश्नार्थक व नकारात्मक वाक्यामध्ये करतात.
4. shall, will यांचा उपयोग Future Tense मध्ये करतात.
5. should यांचा उपयोग उपदेश/ सल्ला देण्यासाठी करतात.
6. would यांचा उपयोग भुतकालीन सवय, भुतकाळात वारवांर घडलेली क्रीया दर्शविण्यासाठी ,तसेच shall/will चा भुतकाळ म्ह्णुन वापरतात.
7. can, could क्षमता(ability) व्यक्त करण्यासाठी
8. may परवानगी(Permission), शक्यता(Possibility) व्यक्त करण्यासाठी.
9. might संभाव्यता(Probability)व्यक्त करण्यासाठी.
10. must बंधनकारकता (Obligation, Compulsion)व्यक्त करण्यासाठी.
11. have,has यांचा उपयोग Present Perfect Tense मध्ये करतात.
12. had चा उपयोग Past Perfect Tense मध्ये करतात.
13. be चा उपयोग Future Continuous Tense / Simple Future च्या Passive Voice मध्ये करतात.
14. being चा उपयोग (Present,Past)Continuous Tense च्या Passive Voice मध्ये करतात.
15. been चा उपयोग (Present/Past/Future) Perfect Tense च्या Passive Voice मध्ये करतात.
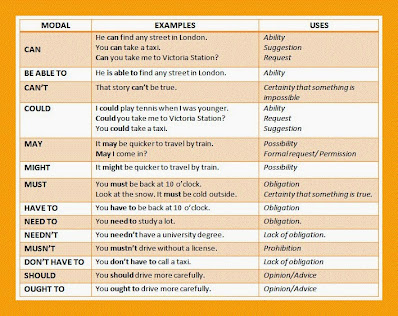
1. Rewrite sentences using proper modal auxiliary.
| Condition | Use of Modal Auxiliaries |
| a) It is very essential for students to learn calligraphy. | Students must learn calligraphy. |
| b) It is possible for students to improve their handwriting with practice. | Students may improve their handwriting with practice. |
| c) My handwriting probably will turn wobbly, if I do not write regularly. | My handwriting might turn wobbly, if I do not write regularly. |
| d) Nowadays it is needed to use computer technology in education. | Nowadays we have to use computer technology in education. |
| e) In future the electronic gizmos are sure to create wonder. | In future the electronic gizmos will create wonder. |
| f) We better keep ourselves updated in the use of computers. | We should keep ourselves updated in the use of computers. |
Fill in the blanks with appropriate modals according to the situations given in the following sentences.
(1) Take an umbrella. It …….rain later.
(2) People …….walk on the grass.
(3) ……I ask you a question?
(4) The signal has turned red. You ……..wait.
(5) I was a sportsperson in my school days. I ……to play badminton.
(6) I am going to the library. I ……. find my friend there.
(1) Take an umbrella. It may rain later.
(2) People should walk on the grass.
(3) May I ask you a question?
(4) The signal has turned red. You must wait.
(5) I was a sportsperson in my school days. I would / used to play badminton.
(6) I am going to the library. I will find my friend there.
Frame Sentences with Modal Auxiliary
Frame sentences by using modal auxiliary for the following predicate.
wear helmet
complete assignment
reach in time
sit here
rain today as sky is cloudy
break a piece of ice
join the excursion
pass std 11 in 2023

Nice exercise based on verbs.