Here are five sets of questions with answers on language study for Std 10, MS Board
Set 1
(A1) Do as Directed (any four): [04 Marks]
i. Write two compound words of your own.
Snowfall, Bookshelf
ii. Pick out the gerund from the following sentence:
This attitude of taking destroys families.
Gerund: taking
iii. Punctuate the following sentence:
after all he doesnt pay me
After all, he doesn’t pay me.
iv. Form two present participles in which the last letter is doubled.
Running, Dropping
v. Complete the following word chain of verbs:
Examine, e_________________, __________________, __________________, ___________________
Examine, Educate, Encourage, Endure, Explore
(A2) Do as Directed (any two): [04 Marks]
i. Change the following sentences into indirect speech:
Robert asked, “Joan, how old are you?”
“I am 13 years old,” she replied.
Robert asked Joan how old she was. Joan replied that she was 13 years old.
ii. Make sentences of your own to show the difference in homophones:
Feet: My feet were cold after walking barefoot.
Feat: Climbing Mount Everest was a great feat.
iii. Rewrite the sentence in present perfect tense:
I had been working for Anil for almost a month.
I have been working for Anil for almost a month.
(A3) Do as Directed (any one): [02 Marks]
i. Begin the sentence with “No sooner ________.”
As soon as the thief escaped, the family informed the police.
No sooner did the thief escape than the family informed the police.
ii. Change the following sentence into positive and comparative degree:
It is one of the best decisions I have ever made.
Positive: Very few decisions I have ever made are as good as this one.
Comparative: This decision is better than most others I have ever made.
Set 2
(A1) Do as Directed (any four): [04 Marks]
i. Write two compound words of your own.
Toothbrush, Sunlight
ii. Pick out the gerund from the following sentence:
Reading improves vocabulary.
Gerund: Reading
iii. Punctuate the following sentence:
the teacher said why are you late today
The teacher said, “Why are you late today?”
iv. Form two present participles in which the last letter is doubled.
Hopping, Planning
v. Complete the following word chain of verbs:
Apply, y_________________, __________________, __________________, ___________________
Apply, Yield, Dance, Eat, Travel
(A2) Do as Directed (any two): [04 Marks]
i. Change the following sentences into indirect speech:
James said, “Can you help me?”
James asked if I could help him.
ii. Make sentences of your own to show the difference in homophones:
Plain: The plain dress looked elegant.
Plane: The plane landed safely.
iii. Rewrite the sentence in present perfect tense:
They had completed their homework before the deadline.
They have completed their homework before the deadline.
(A3) Do as Directed (any one): [02 Marks]
i. Begin the sentence with “No sooner ________.”
As soon as the rain started, the players stopped the match.
No sooner did the rain start than the players stopped the match.
ii. Change the following sentence into positive and comparative degree:
This is the most beautiful painting in the gallery.
Positive: No other painting in the gallery is as beautiful as this one.
Comparative: This painting is more beautiful than any other painting in the gallery.
Here are three additional sets with a variety of grammatical topics like alphabetical order, infinitives, articles, and prepositions.
Set 3
(A1) Do as Directed (any four): [04 Marks]
i. Arrange the following words in alphabetical order:
People, Problem, Pressure, Prosper
Alphabetical Order: People, Pressure, Problem, Prosper
ii. Pick out the infinitive from the following sentence:
He wants to complete the project today.
Infinitive: to complete
iii. Insert suitable articles in the sentence:
He went to __ park and saw __ elephant.
He went to the park and saw an elephant.
iv. Use the correct preposition to fill the blank:
He is good __ mathematics.
He is good at mathematics.
v. Complete the word chain of adjectives:
Clever, R_________________, __________________, __________________, ___________________
Clever, Respectful, Fearless, Small, Lazy
(A2) Do as Directed (any two): [04 Marks]
i. Change the following sentences into indirect speech:
John said, “I will call you tomorrow.”
John said that he would call me the next day.
ii. Make sentences of your own to show the difference in homophones:
Tale: She told us an interesting tale about her travels.
Tail: The cat wagged its tail happily.
iii. Rewrite the sentence in present perfect tense:
We had visited the museum last year.
We have visited the museum last year.
(A3) Do as Directed (any one): [02 Marks]
i. Begin the sentence with “No sooner ________.”
As soon as the bell rang, the students rushed out.
No sooner did the bell ring than the students rushed out.
ii. Change the following sentence into positive and comparative degree:
This is the fastest car I have ever driven.
Positive: No other car I have ever driven is as fast as this one.
Comparative: This car is faster than any other I have ever driven.
Set 4
(A1) Do as Directed (any four): [04 Marks]
i. Write two compound words of your own.
Notebook, Sunrise
ii. Pick out the gerund from the following sentence:
Swimming is a good exercise for health.
Gerund: Swimming
iii. Punctuate the following sentence:
where are you going asked the policeman
“Where are you going?” asked the policeman.
iv. Use the correct article to fill the blank:
It is __ honor to meet you.
It is an honor to meet you.
v. Complete the word chain of nouns:
Flower, R_________________, __________________, __________________, ___________________
Flower, Rose, Elephant, Tiger, Rock
(A2) Do as Directed (any two): [04 Marks]
i. Change the following sentences into indirect speech:
“Are you coming to the party?” Sam asked Sarah.
Sam asked Sarah if she was coming to the party.
ii. Make sentences of your own to show the difference in homophones:
Break: The workers took a short break during the meeting.
Brake: He applied the brake to stop the car.
iii. Rewrite the sentence in present perfect tense:
They had already left when I arrived.
They have already left when I arrived.
(A3) Do as Directed (any one): [02 Marks]
i. Begin the sentence with “No sooner ________.”
As soon as she opened the door, the dog ran out.
No sooner did she open the door than the dog ran out.
ii. Change the following sentence into positive and comparative degree:
This is the largest room in the house.
Positive: No other room in the house is as large as this one.
Comparative: This room is larger than any other room in the house.
Set 5
(A1) Do as Directed (any four): [04 Marks]
i. Arrange the following words in alphabetical order:
Advice, Adjust, Absent, Allow
Alphabetical Order: Absent, Adjust, Advice, Allow
ii. Pick out the infinitive from the following sentence:
She decided to learn French.
Infinitive: to learn
iii. Insert suitable articles in the sentence:
She bought __ umbrella from __ shop.
She bought an umbrella from a shop.
iv. Use the correct preposition to fill the blank:
The cat is hiding __ the table.
The cat is hiding under the table.
v. Complete the word chain of verbs:
Talk, K_________________, __________________, __________________, ___________________
Talk, Knit, Teach, Heal, Laugh
(A2) Do as Directed (any two): [04 Marks]
i. Change the following sentences into indirect speech:
Rachel said, “I have completed the assignment.”
Rachel said that she had completed the assignment.
ii. Make sentences of your own to show the difference in homophones:
Hour: It took us an hour to finish the project.
Our: This is our favorite place to relax.
iii. Rewrite the sentence in present perfect tense:
I had never seen such a beautiful sunset before.
I have never seen such a beautiful sunset before.
(A3) Do as Directed (any one): [02 Marks]
i. Begin the sentence with “No sooner ________.”
As soon as the alarm went off, he woke up.
No sooner did the alarm go off than he woke up.
ii. Change the following sentence into positive and comparative degree:
This is the most exciting book I have ever read.
Positive: No other book I have ever read is as exciting as this one.
Comparative: This book is more exciting than any other I have ever read.
Language Study Std 10
Unique Consonant Blends
Introduction
Blends are combinations of two consonants where each sound can still be heard. For example, in the word “black,” the letters bl form a blend because both the “b” and “l” sounds are pronounced.
Here’s a list consonant blends, along with sentences showcasing the blends in context and more organizational option.
List of Blends
Bl
black, blue, blanket, bloom, blast, blind, blink, blame, bleed, block, blush, blouse, bleach, blend, blizzard, blister, blubber, blurt, bleak, blazing, blindfold, blithe, blueprint, blob, bloom
Cl
class, clock, climb, clear, close, clever, clip, click, cliff, clutch, clue, clash, clover, clump, clench, cling, cloak, clamor, clasp, cloud, clown, clamp, cluster, clatter, clink, clarity
Fl
flower, flame, fly, float, flash, flock, flute, floor, flee, flare, flip, fluff, flake, flood, fluent, flick, flourish, flashback, flinch, flap, flesh, fleet, flutter, floodgate, floppy, flameproof
Gl
glass, glow, globe, glitter, glide, glance, glove, glue, glimmer, gloomy, gleam, glacier, glaring, glaze, glimpse, glorify, glamorous, gloss, gleaming, glidepath, glisten, glowworm, globule
Pl
plane, play, plate, plum, plant, plank, plot, plug, pluck, plow, plunge, plead, pleasant, plankton, plop, plaster, playful, plummet, pliable, plastic, plasma, platter, plume, placid
Sl
slide, slow, sleep, slipper, slim, slap, slant, slip, sled, slice, slick, sling, sloth, slay, slit, slumber, slime, sly, sloppy, slump, sliver, slate, slander, sluggish
Br
brick, brave, brush, bright, break, branch, brass, bring, breeze, brow, brisk, broth, braid, bronze, brood, brisket, brittle, bracket, broad, brag, broker, bramble, brusque
Categorized List
Nature
Bl: bloom, blizzard, bleak
Cl: cloud, clover, cliff
Fl: flower, flock, flood
Gl: glacier, globe, glowworm
Pl: plant, plum, plankton
Sl: sloth, slime, sliver
Objects
Bl: blanket, blouse, blueprint
Cl: clock, clamp, clip
Fl: flute, floor, flash
Gl: glass, glove, globule
Pl: plane, plate, plug
Sl: sled, slate, slipper
Br: brick, branch, bracket
Actions
Bl: blink, blend, blister
Cl: climb, cling, clench
Fl: float, flip, flutter
Gl: glide, glance, glimmer
Pl: plunge, pluck, plaster
Sl: slide, slip, slumber
Br: bring, break, brood
Sentences Using the Blends
1. The black blanket was soaked after the blizzard.
2. The cat climbed the cliff, looking for shelter under the clouds.
3. The flock of birds fluttered near the flower-filled field.
4. She used a glass globe to glimpse into the future.
5. The plane flew over a plum orchard near the plank bridge.
6. The baby giggled as he slid down the slick slide.
7. The brave boy picked up a brick to defend himself from danger.
Creative Activities
1. Word Matching Game: Match blends with their objects/actions:
bl → blink, black
sl → slip, slim
Here’s a worksheet to help learners practice blends effectively:
Blends Worksheet
Part 1: Fill in the Blanks
Fill in the blanks with words that start with the given blends:
1. Bl: The sky turned ___ as the storm approached.
2. Cl: Please use the paper ___ to hold the sheets together.
3. Fl: The butterfly began to ___ gracefully in the garden.
4. Gl: The diamonds on her necklace started to ___ under the light.
5. Pl: Farmers use a ___ to prepare the soil for planting.
6. Sl: Be careful, the floor is ___ after the rain.
7. Br: The artist used a paint ___ to create a masterpiece.
Part 4:Match the blends
Part 3: Word Creation
Create as many words as you can using these blends:
1. Bl: ________, ________, ________
2. Cl: ________, ________, ________
3. Fl: ________, ________, ________
4. Gl: ________, ________, ________
5. Pl: ________, ________, ________
6. Sl: ________, ________, ________
7. Br: ________, ________, ________
Part 4: Sentences
Write sentences using the following blends:
1. Bl: ___________________________________________
2. Cl: ___________________________________________
3. Fl: ___________________________________________
4. Gl: ___________________________________________
5. Pl: ___________________________________________
6. Sl: ___________________________________________
7. Br: ___________________________________________
Part 5: Find the Words
Search for the blend words hidden in the grid below:
B L A C K S
C L I M B P
F L A M E S
G L O B E F
P L A N T S
S L I D E R
B R I C K S
Conclusion
Congratulations on completing the blends worksheet! Understanding blends helps you read and write words more fluently. Keep practicing to strengthen your skills further. Can you think of more words with blends to add to your vocabulary? Remember, blends are everywhere in the English language, so keep an eye out for them while reading or listening!
Useful Expressions For School Recess and Function.
Here’s a list of sentences students can use during recess and function in a rural school setting. These sentences are simple, conversational, and relevant for everyday interactions:
Useful Expressions For School Recess and Function
General Conversations:
1. “What game should we play today?”
2. “Did you finish your homework?”
3. “Can you help me with this question after lunch?”
4. “What did you bring for lunch today?”
5. “Let’s sit under the tree and chat.”
About Nature and Surroundings:
6. “The weather is so nice today!”
7. “Look at those birds; they’re building a nest!”
8. “The field looks so green after the rain.”
9. “Do you think we can play near the stream after school?”
Playful Conversations:
10. “Let’s race to the big tree!”
11. “I’m the captain of the team today!”
12. “Who wants to play hide and seek?”
13. “I can run faster than you!”
14. “Be careful not to step in the mud!”
Sharing and Learning:
15. “Can I try your lunch? It smells delicious!”
16. “Let’s exchange storybooks tomorrow.”
17. “Did you hear the story from our teacher today?”
18. “Do you want me to show you how to skip stones?”
Compliments and Friendly Remarks:
19. “Your new notebook cover is so nice!”
20. “I like the way you solved that math problem.”
21. “Your idea for the art project was great!”
Here’s an updated list of sentences, including those related to cultural programs, annual day celebrations, and general school activities in rural areas:
General Conversations cultural program:
1. “What time is the cultural program starting?”
2. “Did you practice your dance for Annual Day?”
3. “Who is anchoring the event this year?”
4. “Our team is decorating the stage for the program!”
5. “Are you singing in the choir tomorrow?”
During Practice Sessions:
6. “Let’s rehearse the play one more time.”
7. “Do you remember your lines for the drama?”
8. “Your costume looks amazing for the dance performance!”
9. “The music for the group song is so nice.”
10. “Can you help me with my speech for Annual Day?”
Before and After the Event:
11. “The audience clapped so loudly for your performance!”
12. “I’m so nervous about going on stage!”
13. “Did you see the beautiful decorations near the entrance?”
14. “Our teachers worked so hard to organize this program.”
15. “Let’s take a group photo in front of the stage!”
Other Event-Related Conversations:
16. “The chief guest’s speech was really inspiring.”
17. “Did you enjoy the folk dance performance?”
18. “Who is getting the Best Student Award this year?”
19. “I think our team will win the competition!”
20. “Don’t forget to invite your parents to the program.”
These sentences encourage friendly interactions, help students bond, and promote English usage in informal settings.
How to Complete a Story Using Given Clues
How to Complete a Story Using Given Clues
Writing a story can seem challenging, but with the help of clues, it becomes an exciting exercise. Clues act as guideposts that inspire creativity and provide direction to your story. Here’s a step-by-step guide to completing a story using given clues, followed by two examples to spark your imagination.
Steps to Complete a Story:
1. Understand the Clue: Read the given clue carefully to identify the main idea, characters, or setting . सूचकता समजून घ्या – दिलेली सूचकता काळजीपूर्वक वाचा आणि तिच्यातील मुख्य कल्पना, पात्रे किंवा पार्श्वभूमी ओळखा.
2. Build a Plot: Use the clue as a foundation to plan the beginning, middle, and end of the story. कथानक तयार करा – गोष्टीची सुरुवात, मध्य आणि शेवट कसा असावा, याचे प्राथमिक रूप ठरवा.
3. Add Details: Use vivid descriptions, dialogue, and emotions to make your story engaging. तपशील जोडा – वर्णन, संवाद आणि भावना यांचा समावेश करून गोष्ट अधिक रंजक बनवा.
4. Maintain Coherence: Ensure the story flows smoothly and connects logically to the clue. सुसूत्रता ठेवा – गोष्टीचा प्रवाह नैसर्गिक आणि तार्किक असावा. कोणताही भाग विसंगत वाटू नये.
Example 1:
Clue: A young boy finds a magical key in his backyard.
Story:
One sunny afternoon, 10-year-old Anil was digging in his backyard, searching for worms for his pet bird. To his surprise, his spade hit something hard. Curious, he dug further and unearthed a rusty key with strange symbols. Anil felt a sensation as he held it in his hands.
Later that evening, he noticed the key glowing faintly in the moonlight. Following its light, he discovered a hidden door at the base of the old tamrind tree. With a trembling hand, he inserted the key, and the door creaked open, revealing an underground kingdom filled with talking animals and glittering treasures. Anil learned that the key had chosen him to protect this magical realm from an impending danger.
From that day on, Anil led a double life, balancing his schoolwork with adventures in the magical kingdom.
—
Example 2:
Clue: A letter delivered to the wrong address changes someone’s life.
Story:
Smriti was sipping tea on her balcony when the postman delivered a letter addressed to “Mrs. Anjali Mehta.” Smriti didn’t recognize the name, but the address matched hers. Curious, she opened the envelope and found a heartfelt letter from a man apologizing for a mistake he had made years ago. The letter expressed regret, forgiveness, and a desire to reconnect.
Touched by the sincerity, Smriti decided to find Anjali Mehta. After weeks of searching, she discovered an elderly woman living in a nearby retirement home. Anjali was overjoyed to read the letter—it was from her estranged brother, who she thought had forgotten her.
Smriti’s small act of kindness reunited a family, and Anjali became a close friend. Smriti learned that sometimes, life-changing moments come from unexpected places.
Example 3
Prepare a story beginning with– It was first day of school after a long vacation. I was going to school with my friends…….
It was the first day of school after a long vacation. I was going to school with my friends, feeling a mix of excitement and nervousness. The morning air was fresh, and the streets were buzzing with children dressed in crisp uniforms. As we walked together, we talked about how we spent our holidays—some of us had visited new places, while others stayed home and enjoyed relaxing with family.
When we reached the school gate, everything felt both familiar and new. The walls had been repainted in bright colors, and there was a large banner welcoming us back. The scent of fresh notebooks and polished desks filled the air as we entered our classroom.
The teacher, Miss Ananya, greeted us with a warm smile. She handed us a small quiz about our holidays to break the ice. Just as we were settling in, a new student walked in. His name was Aryan, and he had just moved to our town. He looked shy, but Miss Ananya introduced him warmly and asked him to sit beside me.
During the lunch break, my friends and I invited Aryan to join us. As we shared our snacks and stories, he started opening up, telling us about his old school and how he loved sketching. We were fascinated by his sketches, which he shyly showed us from his notebook.
By the end of the day, the nervousness I had felt in the morning had vanished. The first day of school turned out to be a blend of old friendships, new beginnings, and exciting discoveries. As we walked home together, I realized that this year might just be the best one yet.
Conclusion:
Completing a story from a clue is a fantastic way to unlock your creativity. Remember to let your imagination flow while ensuring the story ties back to the given clue. Try it out, and you might just create something extraordinary!
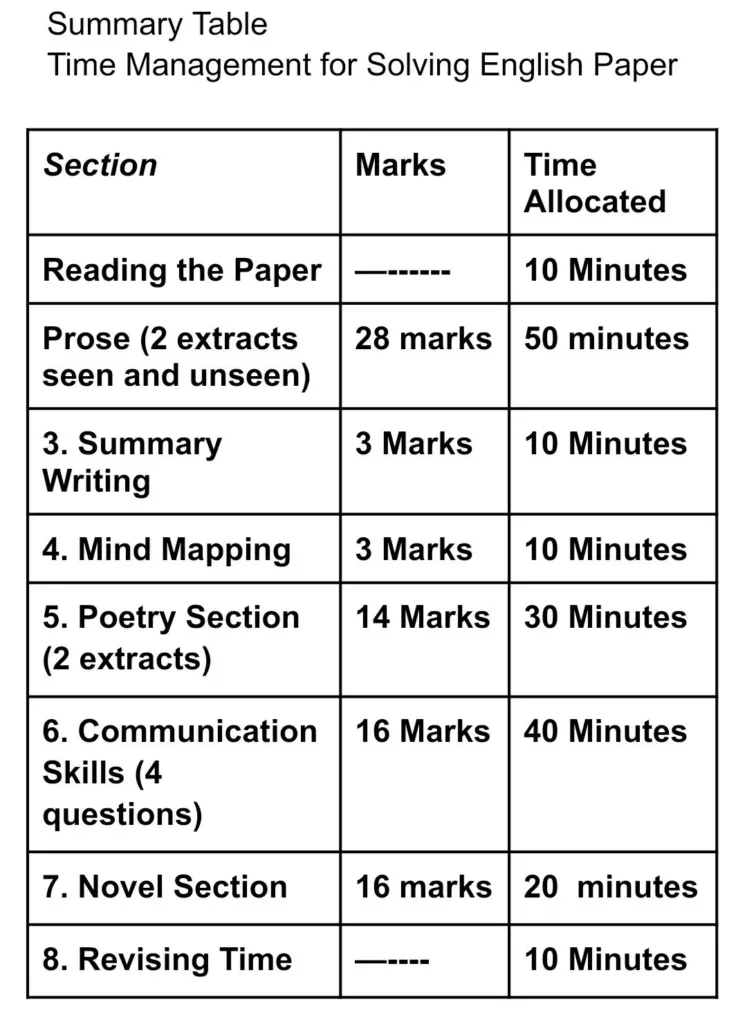
Time Management Plan Std 12 English
Here’s a suggested time management plan for solving an 80-mark English paper for Std. 12 Maharashtra State Board. This strategy divides the time based on the marks allocated and the nature of the questions. You have a total of 3 hours (180 minutes).
1. Reading the Question Paper (10 minutes)
Quickly go through the entire paper to understand the structure.
Identify easy questions and those requiring more time.
2. Prose Section (2 extracts) – 28 marks (50 minutes)
Extract 1: (12 marks)
Spend about 15–18 minutes answering activities like comprehension, grammar, and vocabulary.
Do as directed (4Marks)
2 minutes
Extract 2: (12 marks)
Spend another 15–18 minutes on similar activities.
3. Summary Writing – 3 marks (10 minutes)
Read the passage carefully.
Highlight key points and draft a concise summary.
4. Mind Mapping – 3 marks (10 minutes)
Focus on creativity and clarity.
Use keywords and relevant visuals to organize your ideas.
5. Poetry Section (2 extracts) – 14 marks (30 minutes)
Extract 1 (Activities based on poetry): 10 marks
Spend 12–15 minutes analyzing the extract and solving related activities.
Extract 2 (Poetic Appreciation): 4 marks
Use 10–15 minutes to write an appreciation covering title, theme, poetic devices, and personal response.
6. Communication Skills (4 questions) – 16 marks (40 minutes)
Each question carries 4 marks.
Spend about 10 minutes per question on:
A. Drafting Virtual Messages/ Statement Of purpose/Group Discussion. (04)
B. Email/Report Writing/ lnterview. (04)
C. Speech/Compering/Expansion of Ideas.(04)
D. Review/Blog/Appeal. (04)
7. Novel Section – 16 marks (20 minutes)
Attempt questions based on themes, characters, or events in the novel.
Write concise and to-the-point answers.
8. Revising Time (10 minutes)
Use the remaining time to:
Check for spelling/grammatical errors.
Ensure all questions are attempted.
Refine answers if needed.